
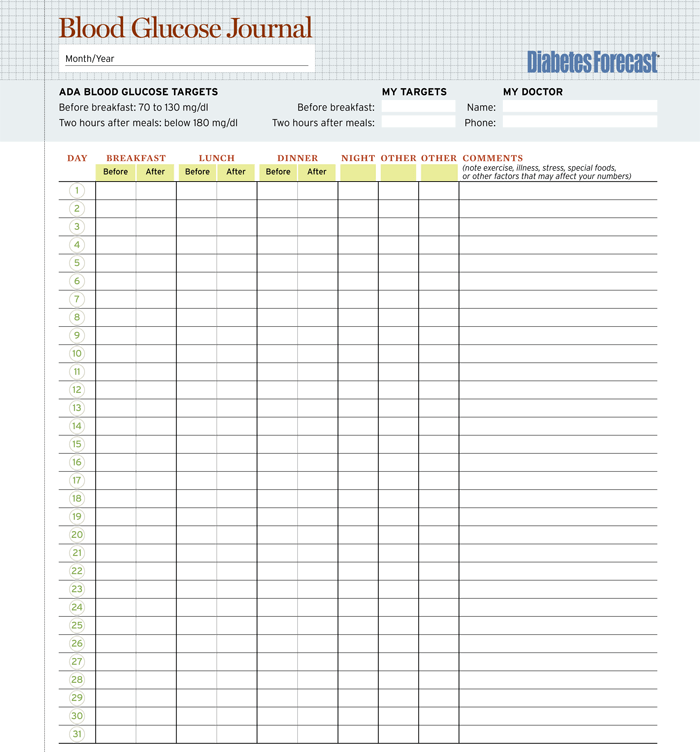
#30 day blood sugar logsheet how to
Mathioudakis says that those with a family history of diabetes - and who show high fasting glucose - should talk with their doctor about how to regulate blood sugar levels. If you need to raise your blood sugar, you should eat a glucose tablet or drink something sugary, such as fruit juice. On the other hand, hypoglycemia is when your blood sugar is too low, typically under 70 mg/dL. To lower blood sugar, you'd want to use more insulin medication to help your cells absorb glucose. If your levels are too high - over 140 mg/dL before a meal or 180 mg/dL after a meal - you may be experiencing hyperglycemia. Most of the time, you'll be able to regulate your blood sugar on your own if it's too high or low. Those with diabetes should get an A1C test at least twice a year - and sometimes every three months. This test reports results as a percentage the higher the percentage, the higher your blood sugar has been in the past three months. If you don't have diabetes, but you may be at risk, your doctor might have you take an A1C test during a yearly check-up. Both devices measure blood sugar with the unit mg/dL, which means a milligram of sugar per deciliter of blood. To check your blood sugar at home, you should use blood glucose tests, such as a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor (CGM). For example, it can be important to use more insulin after a high-sugar meal, or to avoid falling into hypoglycemia while you're sleeping. Day-to-Day Record Chart Try to keep blood sugar levels between 47mmol/l before meals and less than 9.0mmol/l (Type 1) or 8.5mmol/l (Type 2) after meals, most of the time. The timing of these measurements can help determine how much insulin to use.

Typically, this should be done before a meal, one to two hours after a meal, and at bedtime. Type 1 diabetics, along with some type 2 diabetics, who require insulin medication, must check their blood sugar at least four times per day, says Mathioudakis.
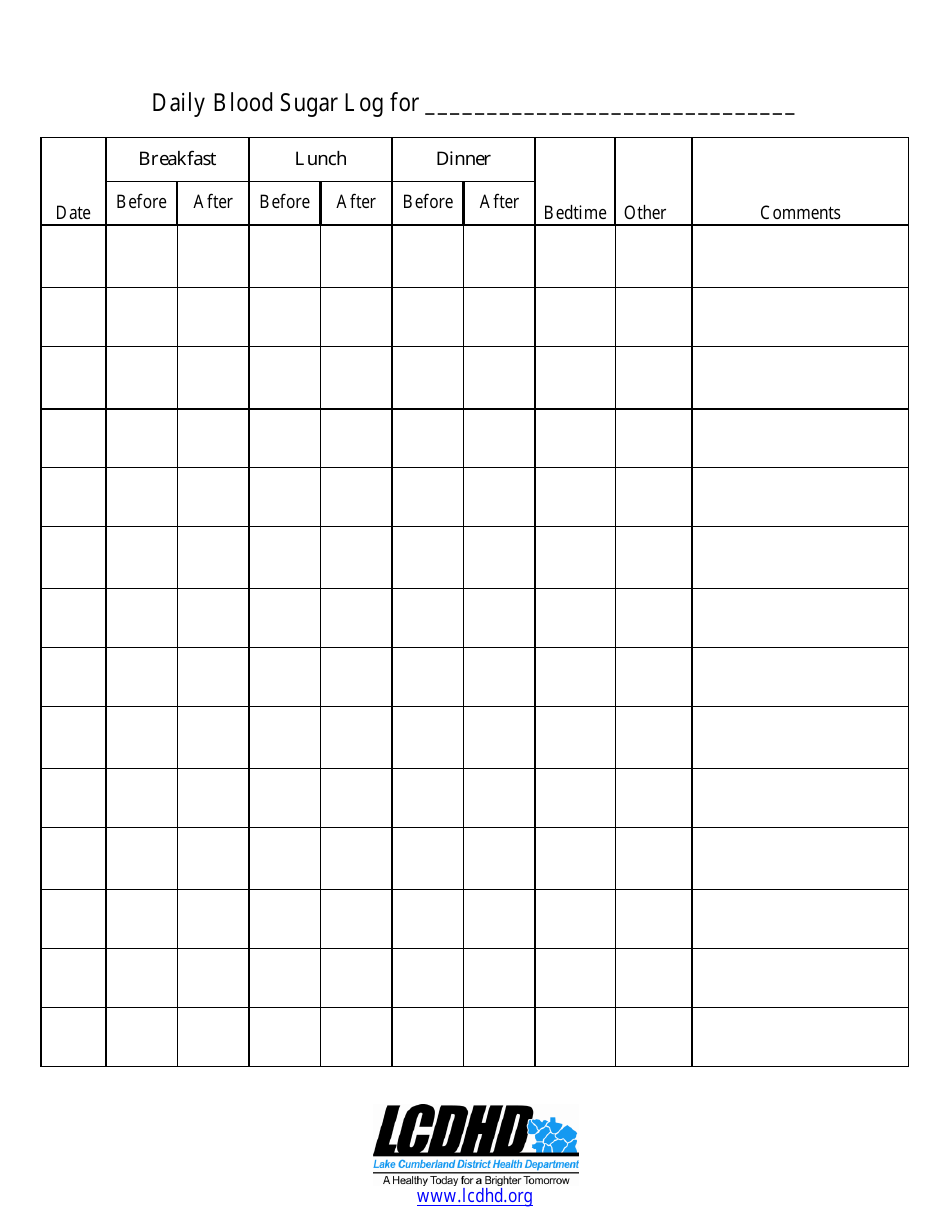
A1C is a blood test, conducted by your doctor, that describes your average blood sugar levels for the past three months. There are many at-home devices - such as finger-prick monitoring kits or continuous glucose monitors - that you can use to measure blood sugar on your own. There are two main ways to check your blood sugar levels:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
